Popover
A popover is a layer that pops up over all other elements on a page.
Live demo
This live demo contains only a preview of functionality and styles available for this component. View the full demo on Storybook for additional information such as its version, controls, and API documentation.
Accessibility testing statusFor every latest release, Carbon runs tests on all components to meet the accessibility requirements. These different statuses report the work that Carbon has done in the back end. These tests appear only when the components are stable.
For every latest release, Carbon runs tests on all components to meet the accessibility requirements. These different statuses report the work that Carbon has done in the back end. These tests appear only when the components are stable.
Overview
A popover is a layer that appears above all other content on the page. Only one popover can appear at a time and can contain varying text and interactive elements. Popovers are used as a base layer in some of our components like tooltips, overflow menus, and dropdown menus.
When to use
- Use when placing interactive elements, like links, buttons, or rich media to make the component more accessible. Disclosures that contain interactive elements use popovers as a base container layer to achieve this accessibility standard. For further guidance on how to display content within a popover, see the disclosure pattern.
- Use when you need to display additional details for specific elements on a page. If your popover exceeds four columns in width, use a modal instead.
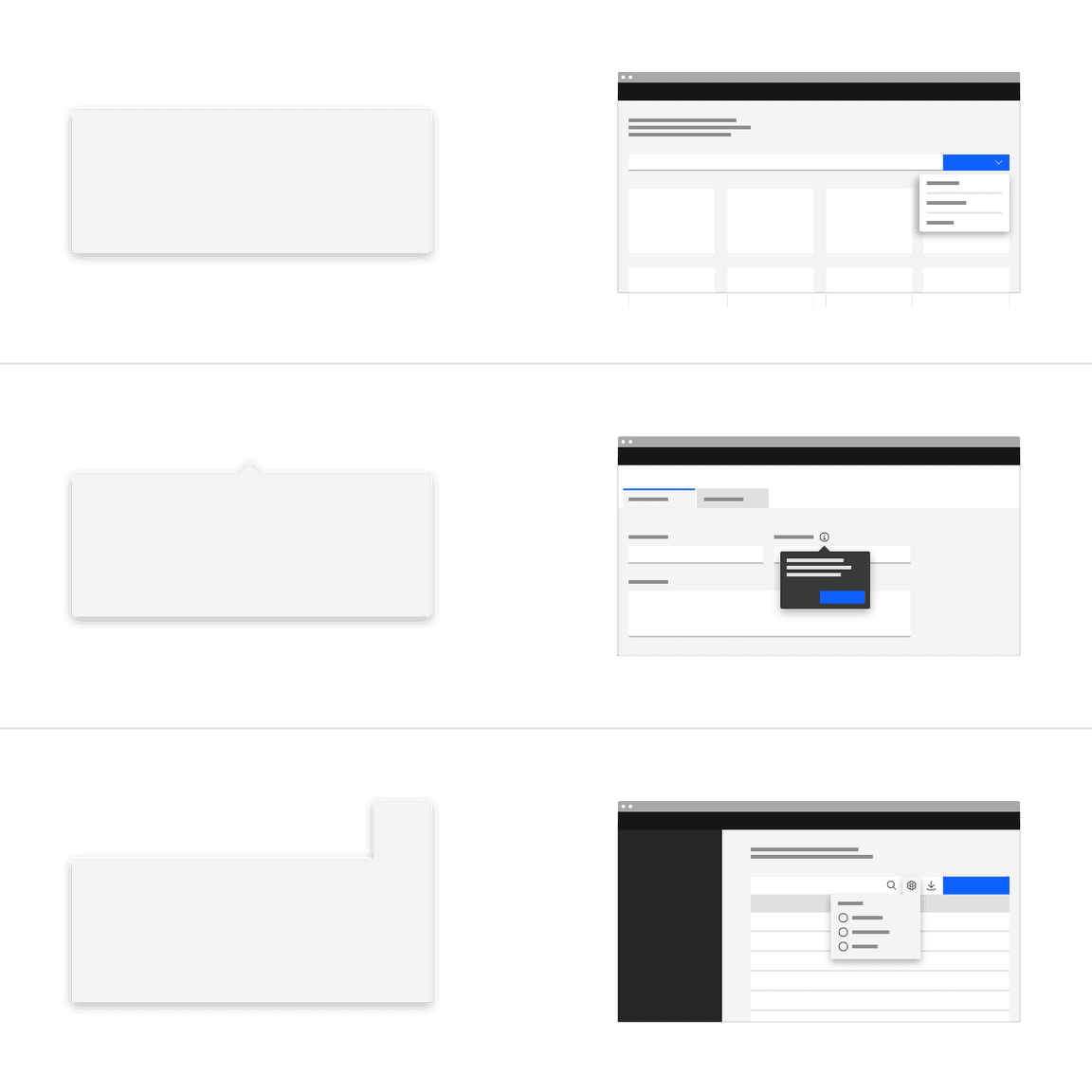
Variants
By default, a popovers structure is made up of a container with no additional tip. Depending on the use case, caret tips or tab tips can be added to the container to help show the relationship between the popover and where it was triggered from.
| Variant | Purpose |
|---|---|
| No tip | Popovers without a tip are typically used when the trigger button has a visually defined down state. |
| Caret tip | Popovers with a caret tip should be used to help show the relationship between the popover and where it was triggered from. A caret tip is typically used when the trigger button does not have a visually defined down state and for icon buttons. |
| Tab tip | Popovers can have a tab tip when the popover is connected to a toolbar or header area. |
Formatting
Anatomy

- UI trigger button: An interactive element that triggers the popover to open on click, hover, or focus.
- Tip: An indicator that is added to a popover container to help show the relationship between the popover and where it was triggered from.
- Content area: An area to place text and interactive elements.
- Container: An area to place text and interactive elements.
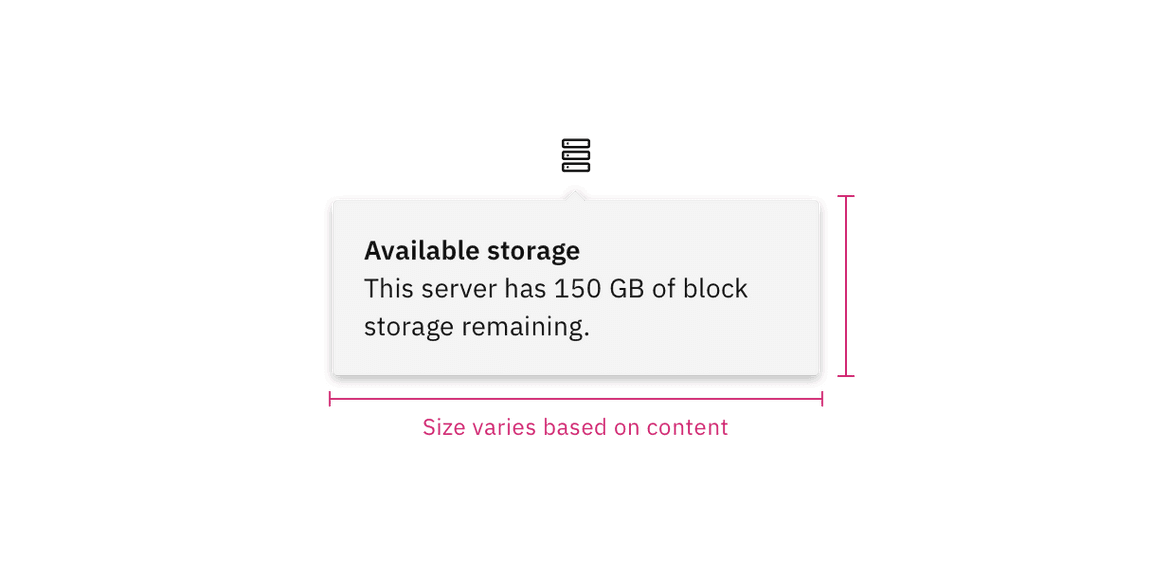
Sizing
Container
The width and height of a popover container can vary depending on the amount of content placed within it. We recommend to not exceed a popover width size of four columns.
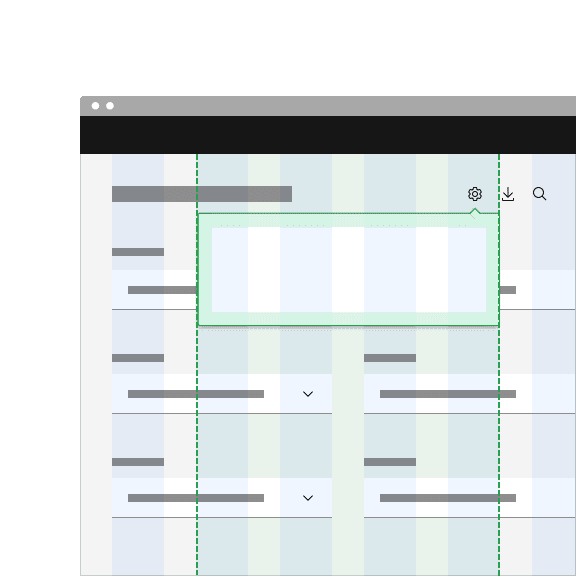
Do keep width between one to four columns.
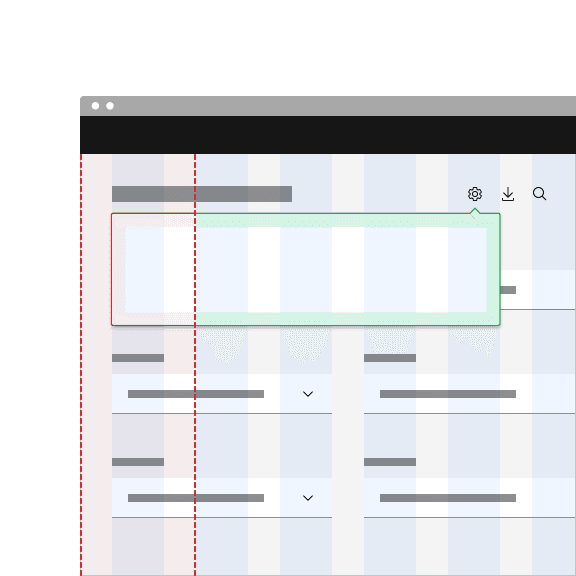
Don't exceed width of four columns.
Trigger button
A popover is controlled by a trigger button. By default, we use an icon button to trigger a popover to open. However, as long as the trigger button is interactive it can visually change its shape and size depending on the usecase.
The trigger button can open the popover on click, hover, or focus depending on what it is being used for. For more information about trigger buttons, see the disclosure pattern.
Content
Main elements
Heading, body, and footer content can vary based on your usecase. To see examples of content used in popovers, see the disclosure pattern.
Overflow content
Scrolling is usually not needed when using a popover. If scrolling is needed, in a dropdown like situation for instance, then the body section should scroll vertically with the header and footer remaining fixed in place if those elements are present. Do not scroll horizontally or let content bleed off the page.
Further guidance
For further content guidance, see Carbon’s content guidelines.
No tip
Popovers without a tip can be used for a wide variety of different use cases. No tip popovers are typically used when the trigger button has a visually defined down state.
Placement
Popover directions by default are set to auto. Upon opening, popovers can detect the edges of the browser to properly be placed in view so the container does not get cutoff. Alternatively, popovers can also specify distinct directions. Direction options vary depending on the popover variant.
When a popover does not have a tip, the trigger button should be flush to the side of the popover. The popover can open from the left, right, bottom, or top of the trigger button.
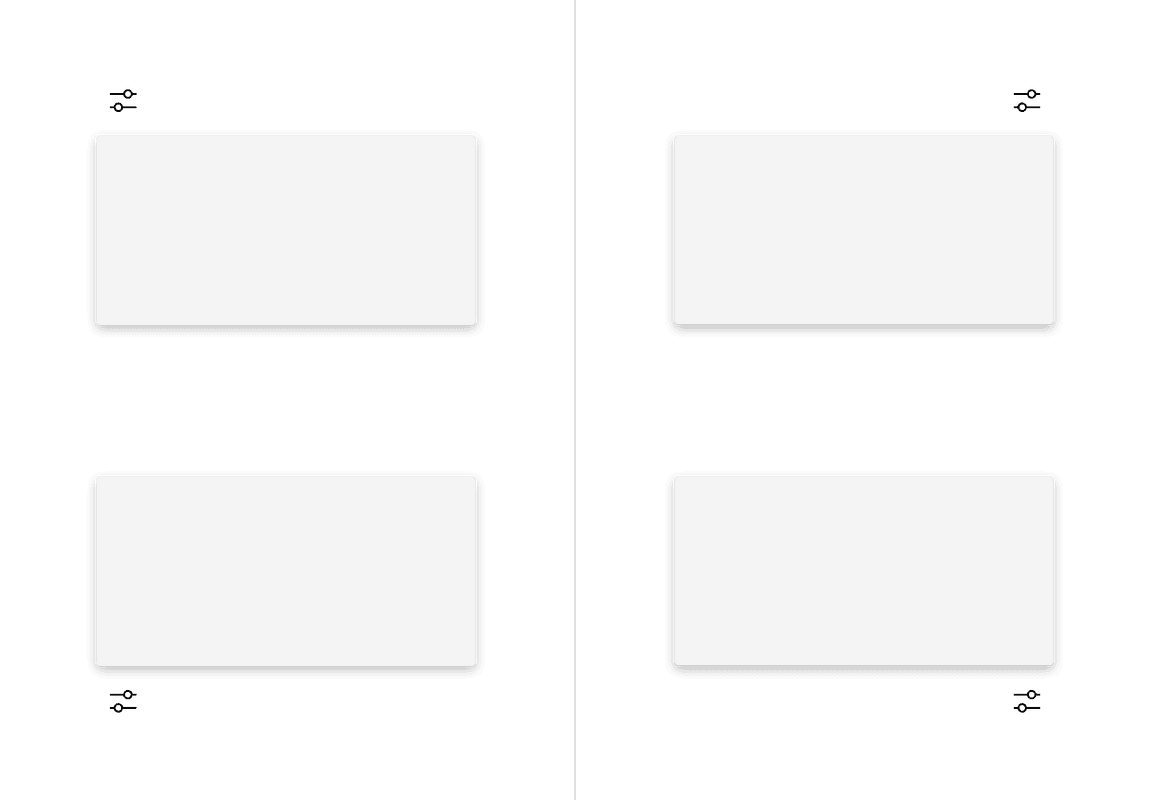
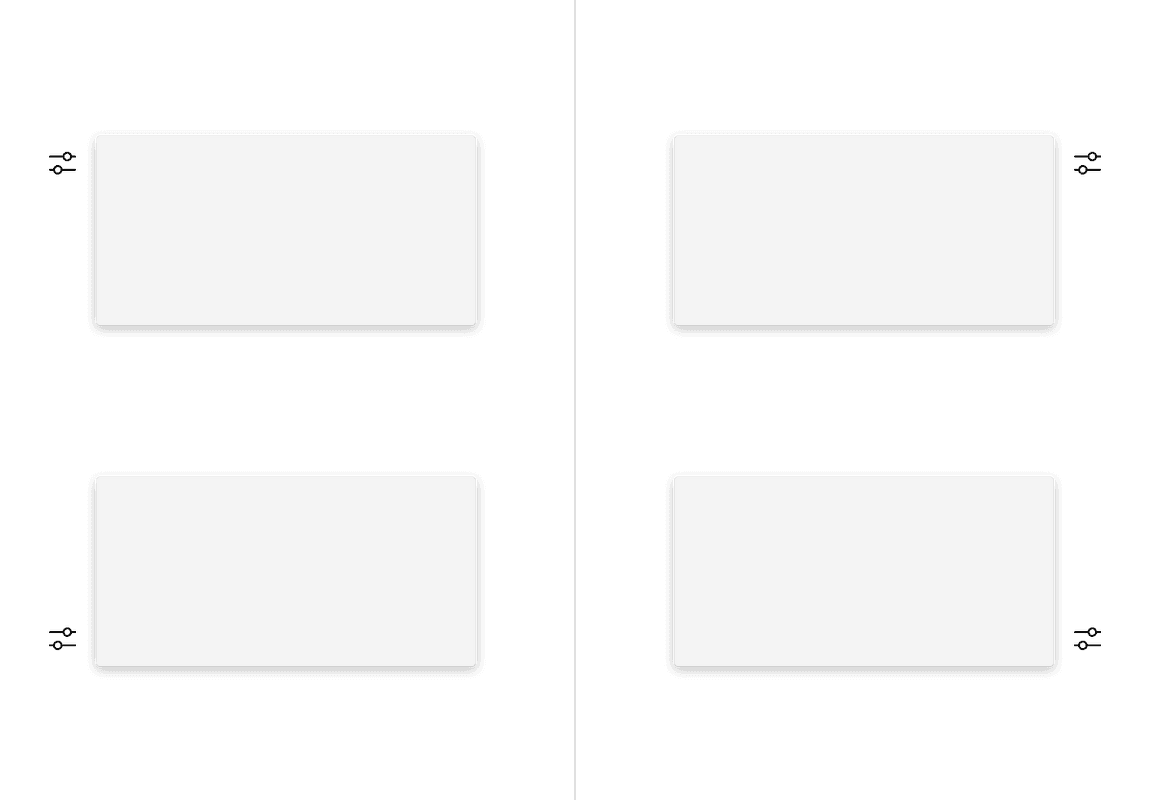
Alignment
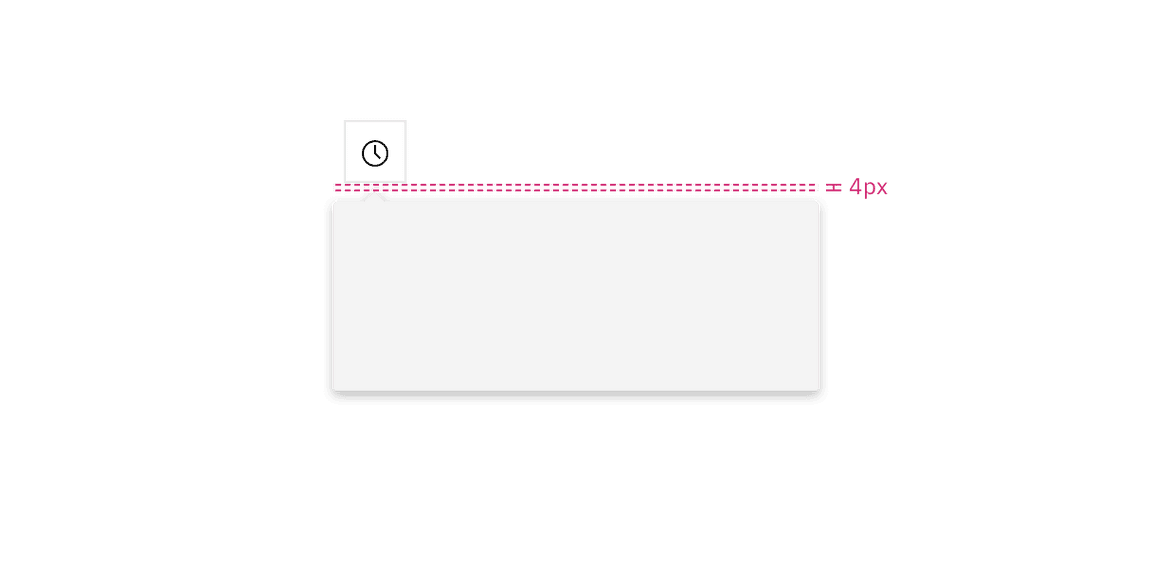
The trigger button should be placed 4px away from the popover container and should always be the same distance away from the popover container regardless of what size button is being used.
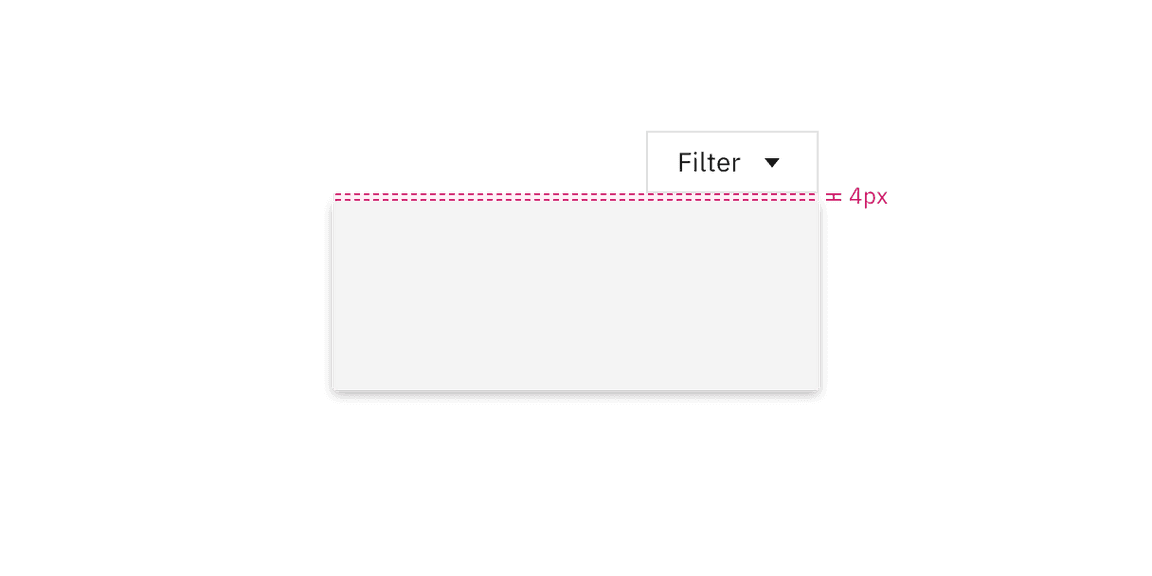
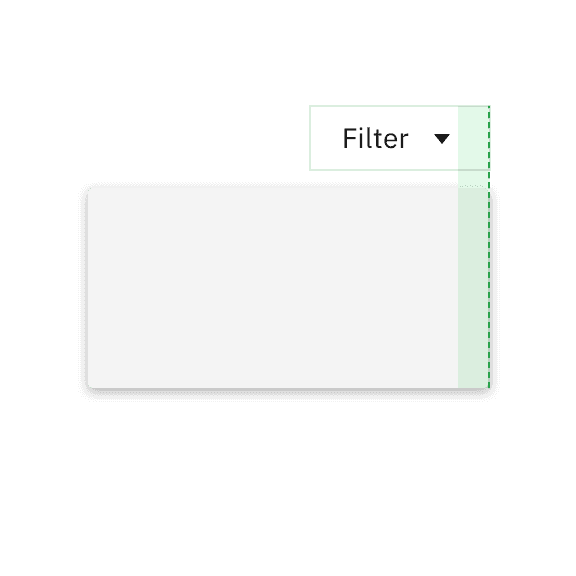
Do flush align the popover edge with the trigger button.
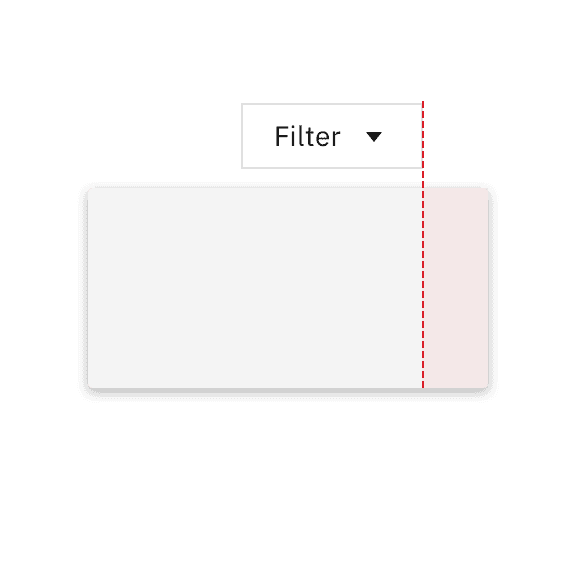
Don't arbitrarily place the popover near the trigger button.
Caret tip
A caret tip should be added to a popover to help show the relationship between the popover and where it was triggered from. A caret tip is typically used when the trigger button does not have a visually defined down state and for icon buttons.
Placement
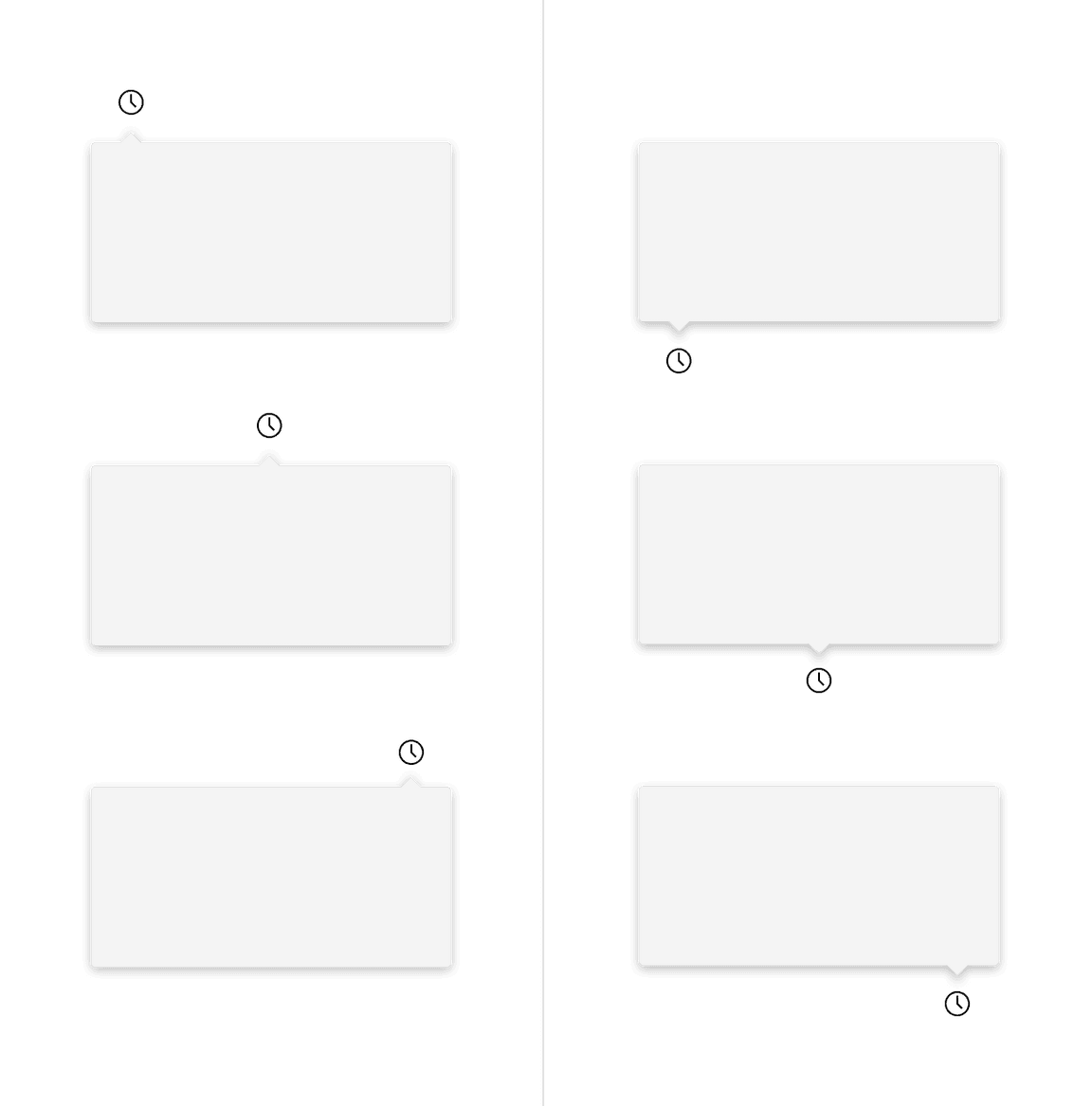
The popover can open from the left, right, bottom, or top of the trigger button. When using a caret tip, the trigger button and caret tip should be vertically center with eachother.
Alignment
The container of the popover may be aligned to start, center, or end to keep the container from bleeding off the page or covering important information.
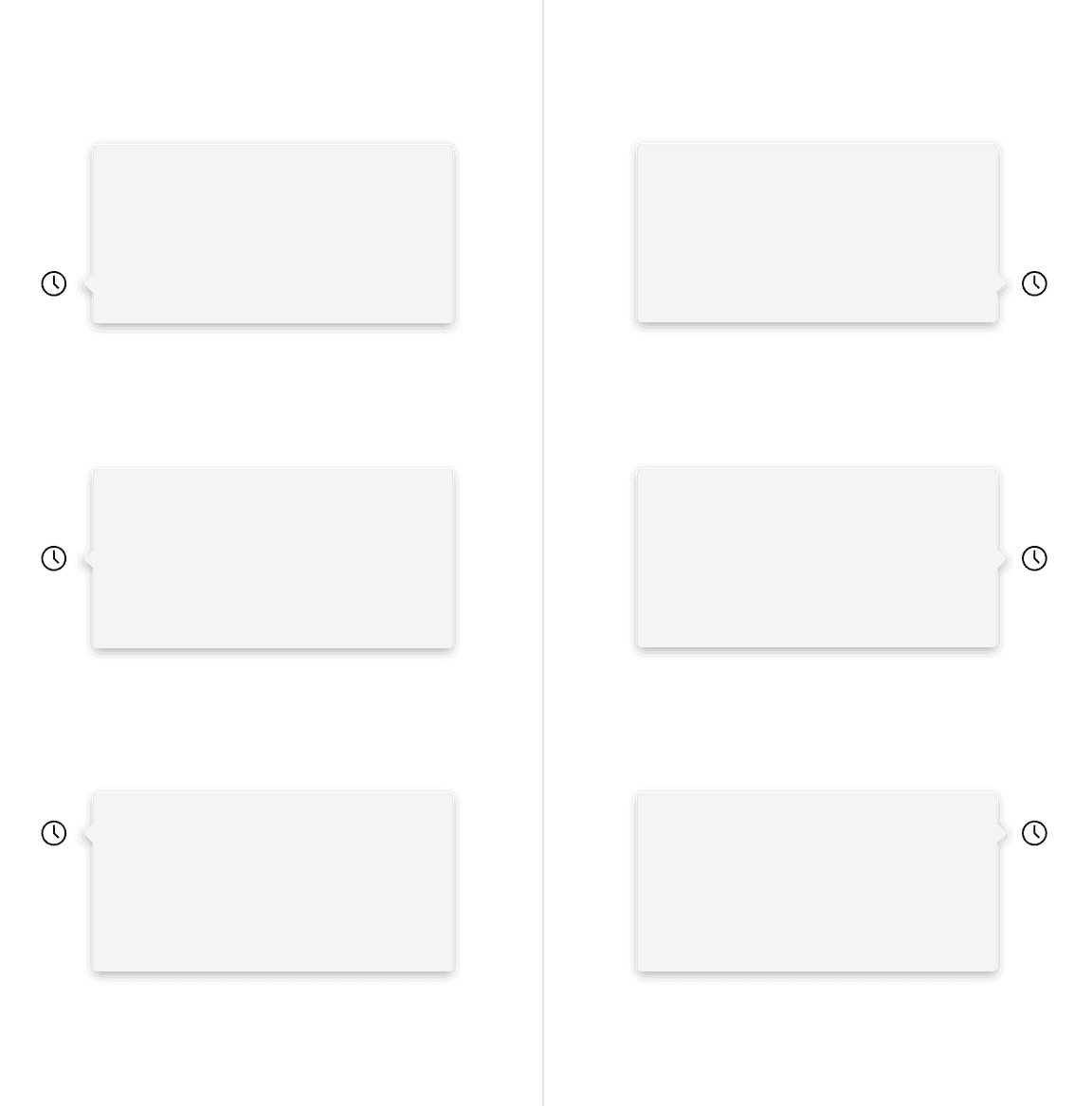
Similarly with no tip popovers, a trigger button paired with a caret tip popover should be placed 4px away from the popover container.
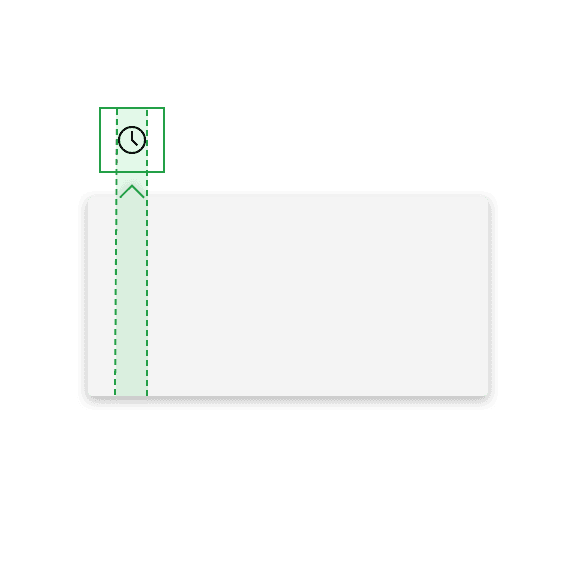
Do align the caret tip center with the trigger button.
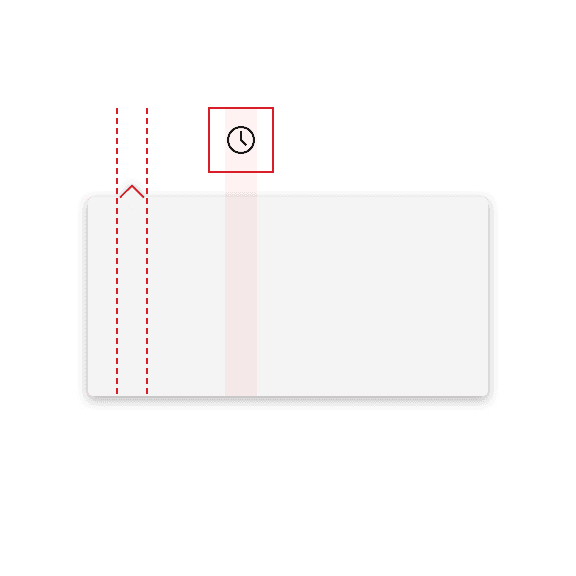
Don't misalign the caret tip with the trigger button.
Tab tip
Popovers can have a tab tip when the popover is connected to a toolbar or header area where the trigger button sits within.
Placement
Tab tip popovers nest within another layer on a page. The tab tip can appear on the left and right of the container and the edges should be flush with the layer edges it sits within.
Alignment
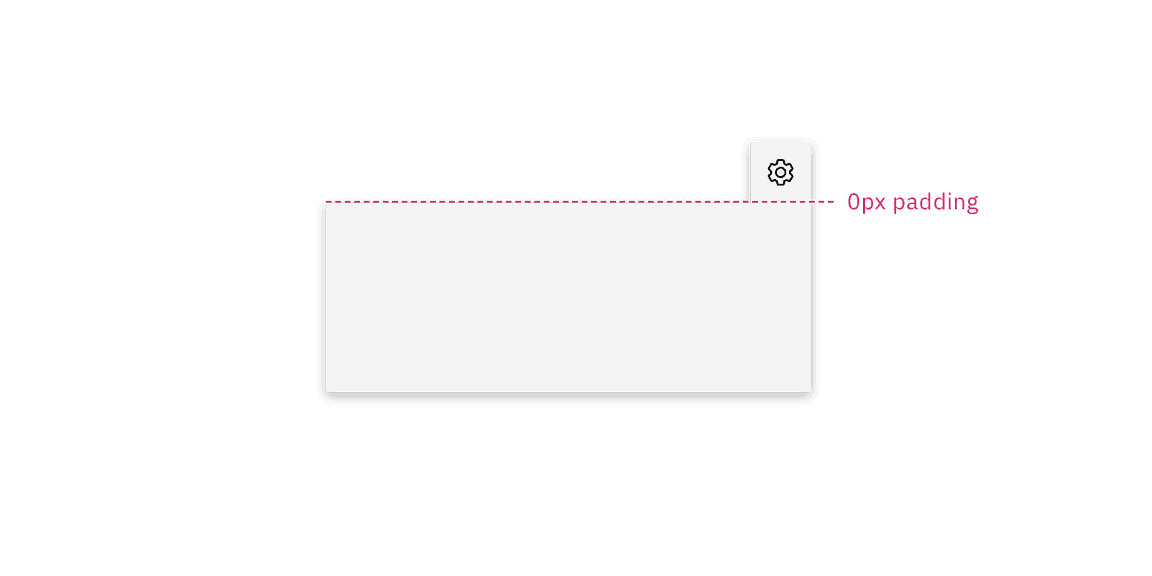
Popovers with a tab tip have 0px space between the trigger button and the container because they are connected to eachother.
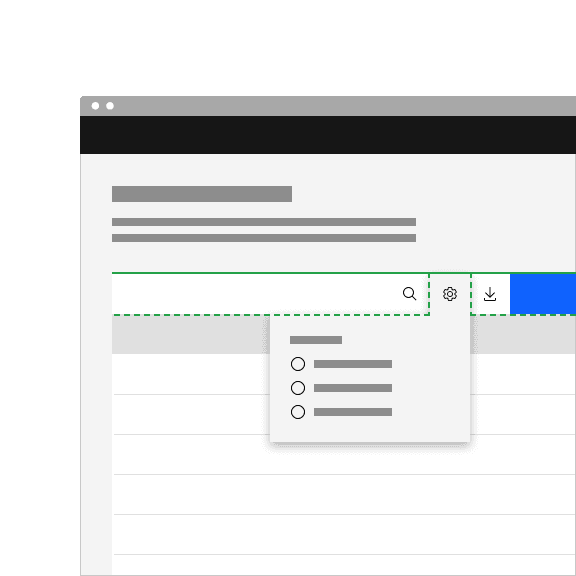
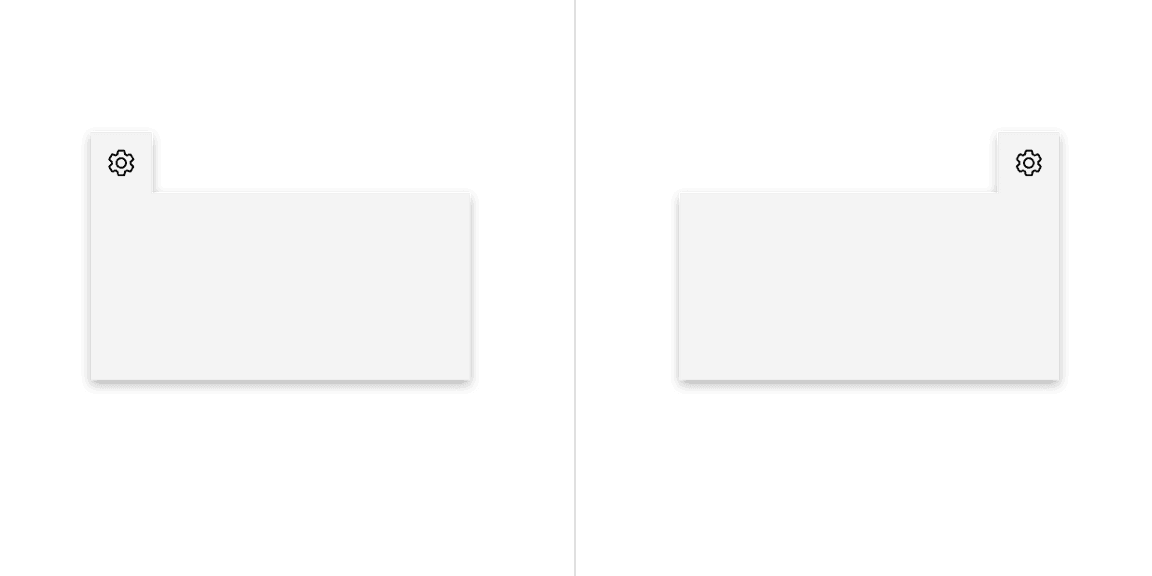
Do top align the tab tip with the layer behind it.
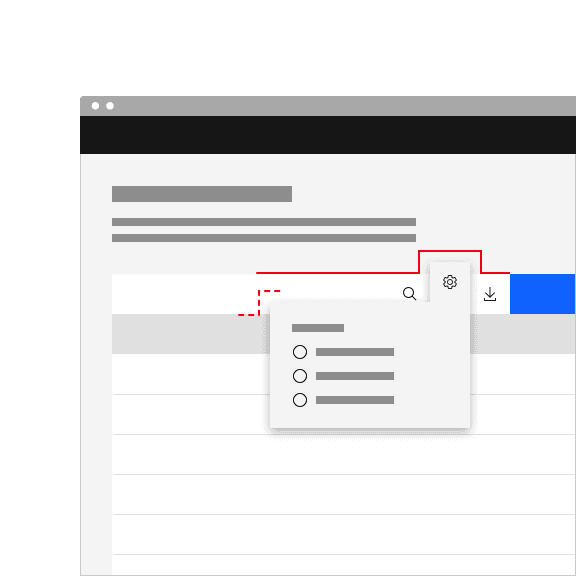
Don't misalign the tab tip with the layer behind it.
Behaviors
Interactions
Mouse
Users trigger a popover to open and close by clicking or hovering on the trigger button depending on the use case.
Click: Open the popover by clicking on the trigger button. Close the popover by clicking on the trigger button again, or anywhere outside of the open popover container.
Hover: Open the popover by hovering over the trigger button. Close the popover by hovering off of the popover or clicking anywhere outside of the open popover container.
Keyboard
Focus: When the popover control has focus Enter or Space activates the
popover control and toggles the visibility of the popover content.
Screen readers
VoiceOver: Users can trigger a button to open a popover by pressing Enter or
Space while the button has focus.
JAWS: Users can trigger a button to open a popover by pressing Enter or
Space while the button has focus.
NVDA: Users can trigger a button to open a popover by pressing Enter or
Space while the button has focus.
Modifiers
Colors
Popovers are most commonly used in these three different container
colors—$layer-01, $layer-02, and $background-inverse.
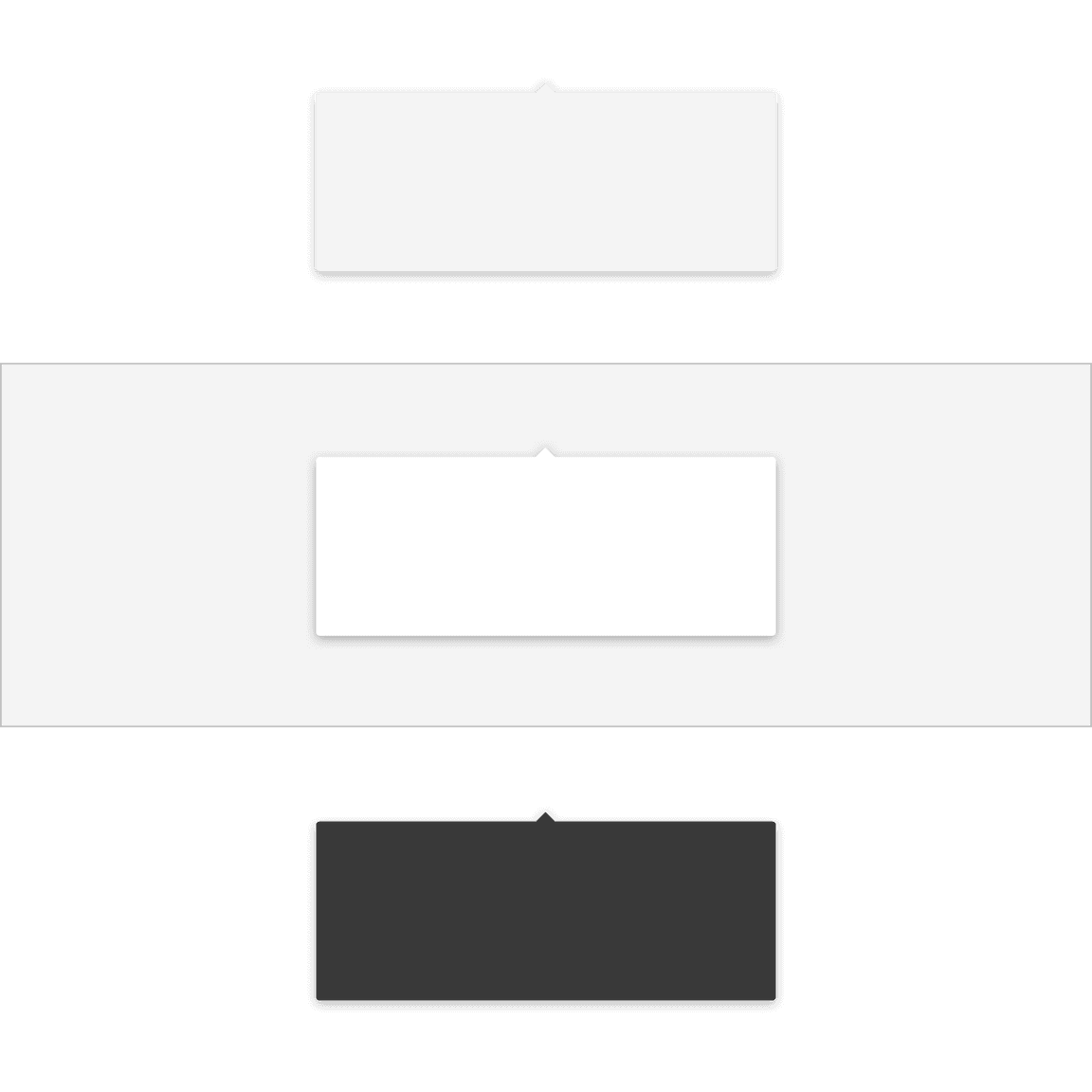
Corners
A popover container has rounded corners by default and the corner radius is set to 2px. Use straight corners when the popover structure contains a tab tip and is connected to a toolbar or header to keep clean lines between the popover and the layer underneath.
Related
Form components
Form components that have menus, like dropdowns, use popovers as a base layer.
Disclosures
Disclosures use popovers as a base layer. Disclosures are comprised of a popover container, text, and interactive elements. For further guidance, see Carbon’s disclosure pattern.
Overflow menus
Overflow menus use popovers as a base layer. When the overflow menu icon button is triggered, the menu opens and uses a tab tip popover as its base. For further guidance, see Carbon’s overflow menu.
Toggletips
Toggletips use the popovers as a base layer. Toggletips allow interactive elements within the popover container while still being accessible. For further guidance, see Carbon’s toggletip component
Tooltips
Tooltips use popovers as a base layer. Tooltips are comprised of a trigger button, popover container and text. For further guidance, see Carbon’s tooltip component.
References
Popup,Component research, (OpenUI)
Disclosure, W3C WAI-ARIA practices, (W3C Working Group Note)
Feedback
Help us improve this component by providing feedback, asking questions, and leaving any other comments on GitHub.